Pipe fittings :-There are various types of pipe fittings used to complete the piping system in the plant. These pipe fittings are used to change direction, change diameter, or to branch off from main run of pipe etc. piping system can not be completed without pipe fittings. Details of the piping fitting are given below
Type of pipe fittings
Elbows
Elbows are used to make 90 deg are 45deg changes in the direction of pipes, there are two types are 90 deg elbows available for use. These are long radius and short radius elbows. The long radius elbow have a bend radius of 1.5D where D is nominal pipe size, whereas the short radius elbows have bed radius of 1D. The 45deg elbows are of 1.5D radius. Any bend with more than 1.5D radius has to be specially made as per requirements.


For large diameter piping, bends are fabricated by profile cutting of pipes and are called mitre bends. Miter bends with two piece, there piece or four piece construction can be made. These are deg. Elbows are also available in cast iron construction. If space permits long radius elbows should be used because, short radius elbows are subject to high stress concentration in the throat of the sharp curvature bend.
Returns
Returns change the direction through 180 deg. This is mainly used in heating coils, heat exchangers, etc. Returns with 1.5D radius and 1D radius are available.
Tees
Tees are used for branching off. For low pressure services, branching off is done by direct welding of branch pipe to run pipe instead of using a standard tee. In certain causes, reinforcing pads are used for structural stability of such connections. The weld tee is expensive. A substitute for the tee is a stub-in ,where the branch is welded directly to the header. If the pressure is high, the stub-in may have to be reinforced.

Some of these are weld saddle, reinforcing pad, weldolet etc. The manufacturing restrictions do not allow reducing tees of all size of reducing tees in the standard, use the thumb rule of dividing the major diameter by 2 and consider the next lower size. In the case of reducing tees and crosses, the size of the largest run opening shall be given first, followed by the size of the opening at the opposite end of the run, were the fitting is a tee, the size of the branch is given last where the fitting is a cross the largest side-outlet is the third direction given, followed by the opening opposite.
Cross
This is a fitting very rarely used in piping system. There are two types of crosses, the straight and reducing, To reduce the inventory, it is preferred to use tees except where space is restricted as in marine piping.

Reducers
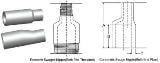
There are two types of reducer concentric reducers and the Eccentric reducers. When the center lines of the larger pipe and smaller pipe are to be maintained same, then concentric reducer are used. When one of the outside surface of the pipe lines are to be maintained same, then eccentric reducers are required. There are no eccentric reducers in socket weld fitting and Swage nipples are used for such service.

The size restrictions for manufacture as explained in Tees is also applicable to reducers. The eccentric reducer cost more than concentric reducer, where ever possible concentric reducer should be used. The eccentric reducer is used mostly in pipe ways or pipe racks. The off set appears in the center line of eccentric reducer ½ the difference of two inside diameters. The eccentrics reducer are used in the pump suction lines to avoid air pockets
cers available, the
Stub Ends
To reduce the cost of piping, stub ends are used with backing flanges for flange joints when exotic materials are used in piping. ASME B16.9 specifies two types of stub ends, the long stub ends and the short stub ends. The length of stub ends as per MSS-SP-43 is the same as that of short stub ends. MSS-SP-43 specifies two classes, Class A with radius and Class B without radius at the corner. Class B can be used with slip-on flangs. Designer selects stub end (long/short) ensuring the weld of pipe to stu end not get covered by flange.

When Class A stub ends are used, the inner diameter of backing flange is chamfered for better seating. The minimum lap thickness should be the same as that of the pipe wall. When special facings such as tongue and groove, male and female etc. are employed additional lap thickness shall be provided. The gasket face finish shall be provided with serrations as required. ASME B 16.9 considered long pattern as the standard when nothing is specified in this respect.
Couplings
Coupling are of three types:
- Full Coupling
- Half Coupling
- Reducing Coupling

Full couplings are used to connect small bore pipes as projection of welding affect the pipe bore, when butt welding is used, reduce the flow area. Half couplings are used for branch connections and reducing couplings for size reduction. Half coupling is mostly used for instrumentation hook ups. Reducing coupling maintain the pipe center lines same and eccentric swage nipples are used to maintain the outside sauce same for such systems
Swage Nipples
Swage Nipples are like reducers but are used to connect butt welded pipe to smaller screwed or socket welded pipe. There are two types of swage nipples, the concentric and the eccentric. Various combinations of end connections are possible in swage nipples. These are designated as
PBE – Plain Both Ends
PLE – Plain Large End
PSE – Plane Small End
BLE – Beveled Large End
TSE -Threaded Small End
Unions
Unions are used in low pressure piping where dismantling of the pipe is required more often as an alternative to flanges. Unions can be with threaded end or with socket weld ends. There are three pieces in a union, two end pieces to attach to the run pipe and the third threaded piece to connect these two. The ball type metal seating ensure sealing.

3 thoughts on “what are pipe fittings used oil and gas industries”